1、 Unqualified terminal retention force
Generally, the unqualified retention force of the terminal in the sheath is due to the design, manufacturing and material use of the harness connector. For standard and qualified connectors, the insertion and removal retention force of connectors with specification spacing less than 2.8 shall be greater than 40N; The retention force of connectors with a spacing greater than 2.8 shall be greater than 60N.
2、 Interposition interference
It refers to that the male end of the harness connector is inserted into the non effective area of the female terminal during the mating process of the male end and female end of the harness connector, which causes the terminal to withdraw its pin and lose its function. It is generally caused by problems in the design and manufacturing process. One is the structural design problem, and the other is the problem of terminal insertion and removal force.
3、 Product application problems
The above two reasons are both caused by the quality problem of the terminal wire itself. It is also caused by the harness in the production process, which generally includes the terminal crimping problem and the terminal assembly problem.
For example, improper crimping leads to excessive bending, which makes the connection area of the terminal not parallel to the center line of the crimping area. The degree of excessive bending easily increases the insertion and extraction force, affecting the assembly performance; In severe cases, the male terminal cannot be inserted into the effective area of the female terminal during the docking process.


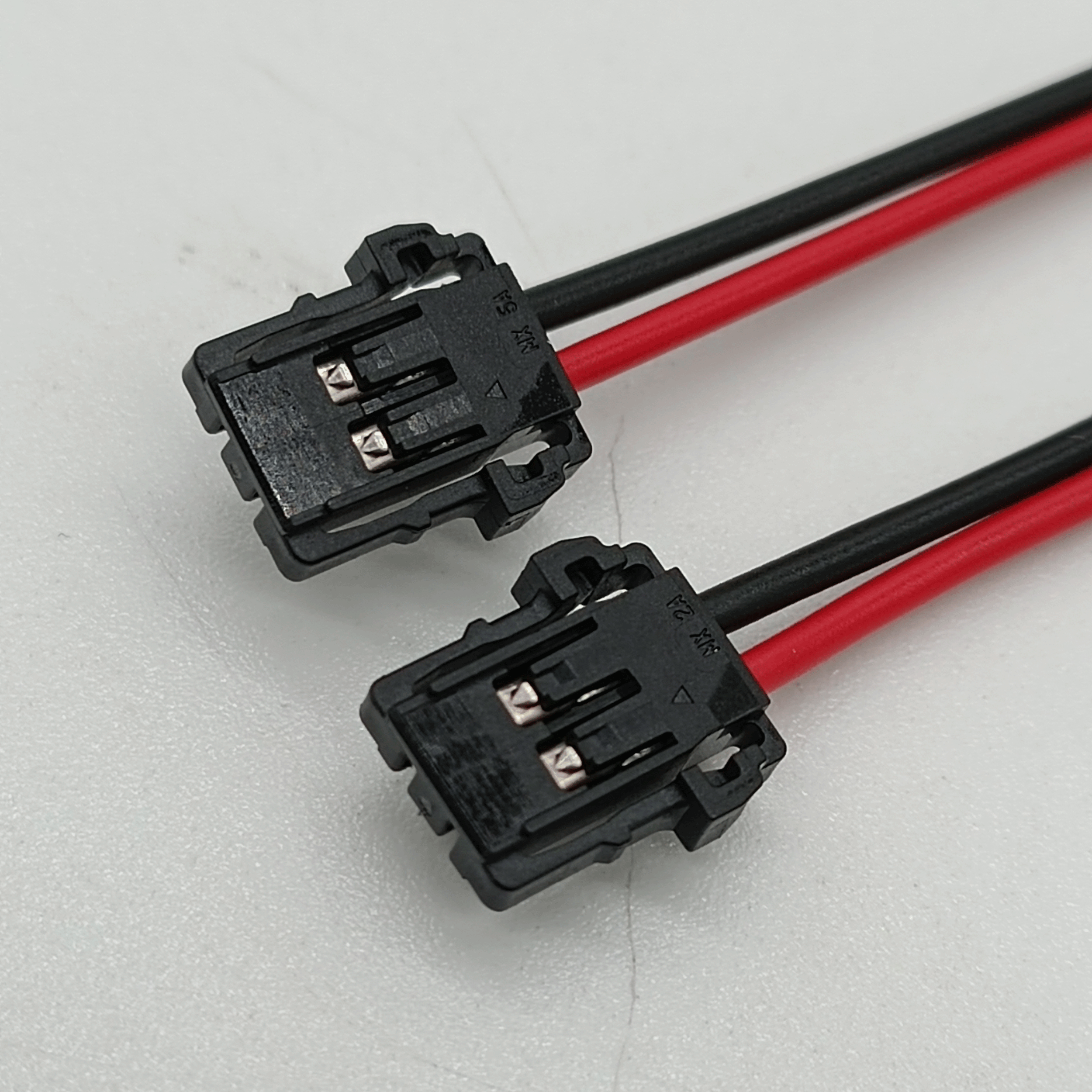
Share:
Function of Terminal Wire Harness Shielding Layer
What problems are easy to occur at the terminal wire connector?